

Why Are There Different Types of Polyester and What Are Their Uses
Polyester is a versatile synthetic fiber that has been widely used in various industries, ranging from fashion to home furnishings. Understanding the different types of polyester is crucial for selecting the right material for specific applications. Each type of polyester has unique properties and characteristics that lend themselves to diverse uses, making this category of fabric significant in both consumer goods and industrial products.
The classification of polyester can be influenced by factors such as fiber structure, production methods, and intended application. From the lightweight and breathable properties of polyester blends used in clothing to the durability and resistance of polyester in industrial applications, recognizing the differences among these variants can enhance decision-making for manufacturers and consumers alike. This exploration not only highlights the significance of different types of polyester but also emphasizes their role in meeting the growing demands of sustainable and innovative solutions in textiles and beyond. Understanding these distinctions opens the door to making informed choices in various sectors where polyester plays a pivotal role.

Types of Polyester: Understanding the Variations
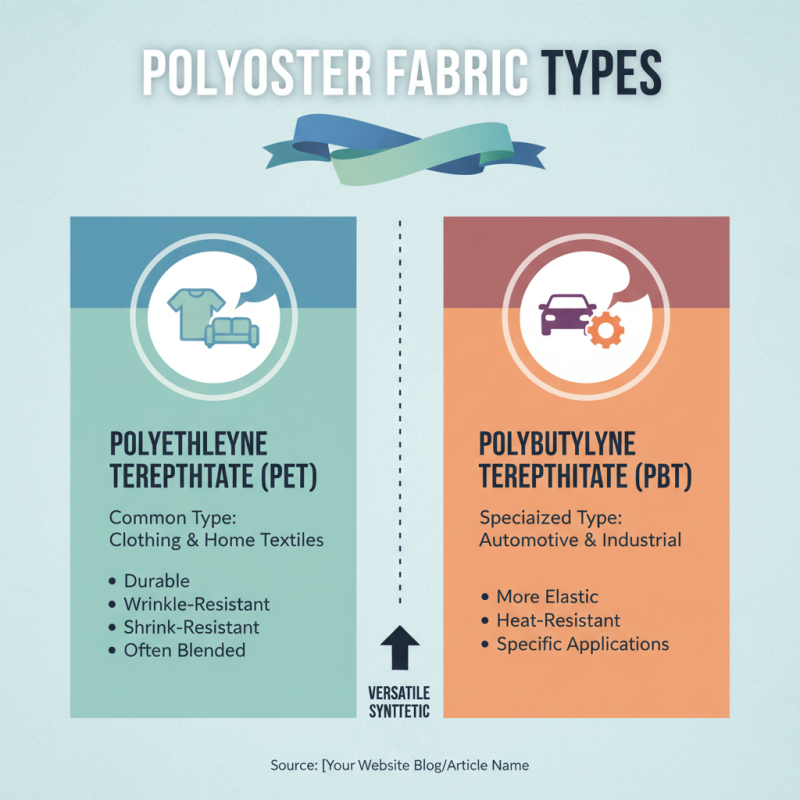
Polyester is a versatile synthetic fabric that comes in several variations, each tailored for different applications. The most common types include polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is widely used in clothing and home textiles due to its durability and resistance to wrinkles and shrinking. PET is often blended with other fibers to enhance its properties. Another variation is polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), which is more elastic and resistant to high temperatures, making it suitable for specialized applications like automotive and industrial uses.
In addition to PET and PBT, there is also recycled polyester, which is made from post-consumer plastic bottles and waste. This sustainable alternative has gained popularity in the fashion and textile industries as environmentally conscious consumers seek eco-friendly materials. Each type of polyester has specific attributes that cater to various sectors, from fashion to furnishings, automotive to engineering, highlighting its adaptability and significance in modern manufacturing. Understanding these variations allows consumers and manufacturers alike to choose the right polyester type for their needs, balancing performance, cost, and sustainability.
Chemical Composition of Different Polyester Types
Polyester is a versatile thermoplastic widely utilized in the textile and industrial sectors, primarily due to its unique chemical composition and properties. The most common form of polyester is polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is created through the polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. This process allows for the creation of polymers that can be processed into fibers, films, and bottles. According to the American Chemical Society, PET accounts for approximately 60% of the total polyester production globally, driven primarily by its use in apparel and packaging industries.
Another significant type of polyester is polylactic acid (PLA), which is derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. PLA is gaining traction in the market due to its biodegradable properties, often utilized in eco-friendly applications such as disposable cutlery and packaging materials. Research conducted by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory indicates that the global PLA market is expected to reach 1.8 billion USD by 2025, highlighting its increasing significance in sustainability-focused development.
In addition to PET and PLA, there are other specialty polyesters such as polybutylene terephthalate (PBT), known for its superior chemical resistance and thermal stability. PBT is widely used in electrical applications, automotive components, and engineering plastics. Reports from the global polyester market indicate a growing demand for high-performance polyesters like PBT, particularly due to the automotive industry’s push for advanced materials that enhance durability while reducing weight, anticipated to drive growth rates of around 6.5% annually through the next decade.
Common Applications of Various Polyester Fabrics
Polyester is a versatile fabric widely utilized across various industries, owing to its unique properties and durability. Different types of polyester fabrics are used for specific applications, catering to diverse needs. For instance, polycotton blends, which combine polyester with cotton, are popular in casual wear and home textiles. This blend offers breathability, softness, and easy care, making it ideal for everyday garments and bed linens.
Another significant type is the recycled polyester, often derived from plastic bottles. This eco-friendly fabric is gaining traction in the fashion and textile industries for products ranging from sportswear to outerwear. Recycled polyester not only helps in reducing waste but also provides moisture-wicking properties, making it suitable for activewear. Additionally, high-tenacity polyester is used in industrial applications, such as tire manufacturing and heavy-duty fabrics, due to its strength and resistance to wear and tear. These different polyester fabrics highlight the adaptability of the material across various markets and consumer needs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Polyester Type
Polyester is a synthetic fabric widely used in the textile industry, and its versatility is attributed to the various types available, each with unique advantages and disadvantages. For instance, PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) is the most common type, known for its excellent durability and resistance to wrinkling. However, it can be less breathable, making it less suitable for hot climates. According to a report from the Textile Research Journal, polyester fabrics can retain shape and elasticity, making them ideal for activewear and outdoor gear.
Another type, PCDT (Poly-1,4-cyclohexylene dimethylene terephthalate), offers a softer feel and improved stretch compared to PET. While it’s more comfortable to wear, PCDT is generally more expensive to produce. Furthermore, its susceptibility to damage from outdoor elements can limit its use in harsher environments. Research indicates that PCDT blends are often preferred for fashion apparel, where comfort is prioritized.
Tips: When selecting polyester for specific applications, consider the environmental conditions and end-use requirements. For sportswear, look for moisture-wicking properties typically found in advanced polyester blends. Always check for certifications regarding breathability and durability to ensure you’re choosing the right fabric for your needs.
Future Trends in Polyester Development and Usage
The future of polyester development is shaped by innovation and sustainability. As environmental concerns continue to rise, the polyester industry is adapting by focusing on eco-friendly materials and production processes. Biodegradable polyesters, derived from renewable resources, are gaining popularity, offering a viable alternative to traditional petroleum-based options. These advances not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also address issues related to waste and pollution associated with synthetic fibers.
Moreover, as the demand for functional textiles increases, polyester is evolving to meet these needs through technological advancements. Innovations such as moisture-wicking properties, enhanced durability, and thermal regulation are being integrated into polyester fabrics, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from athletic wear to home textiles. The incorporation of smart textiles—fabric embedded with technology for monitoring health or environmental conditions—also presents exciting prospects for polyester's role in future markets. This evolution will likely lead to textiles that are not only performance-oriented but also environmentally responsible, shaping a sustainable future for the industry.
Why Are There Different Types of Polyester and What Are Their Uses - Future Trends in Polyester Development and Usage
| Type of Polyester | Characteristics | Common Uses | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | High strength, durability, resistant to shrinking and stretching | Bottles, clothing, containers | Recycling advancements, bio-based production |
| PES (Polyethersulfone) | High thermal stability, chemical resistance | Medical devices, automotive parts | Increased use in high-performance applications |
| PBT (Polybutylene Terephthalate) | Excellent electrical properties, low moisture absorption | Electrical components, automotive parts | Focus on lightweight and recyclability |
| PLA (Polylactic Acid) | Biodegradable, derived from renewable resources | Packaging, disposable cutlery | Expansion in sustainable applications, consumer awareness |
| PES (Polyester Spandex) | Elastic, soft touch, excellent shape retention | Activewear, swimwear, undergarments | Innovations in performance fabrics, eco-friendly versions |
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Yarn Acrylic for Your Next Craft Project
-

Unlocking the Benefits of Acrylic Fiber: Why It's the Future of Sustainable Fashion
-

2025 Top Yarn Acrylic Options for Every Craft and Project
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Staple Fibers for Your Projects
-

10 Best Practices in Textile Manufacturing for Sustainable Production
-

Exploring the Different Types of Textile Fibers: A 2025 Guide to Fabrics